Wireshark Basics
Wireshark is an open-source, cross-platform network packet analyser tool capable of sniffing and investigating live traffic and inspecting packet captures (PCAP). It is commonly used as one of the best packet analysis tools.
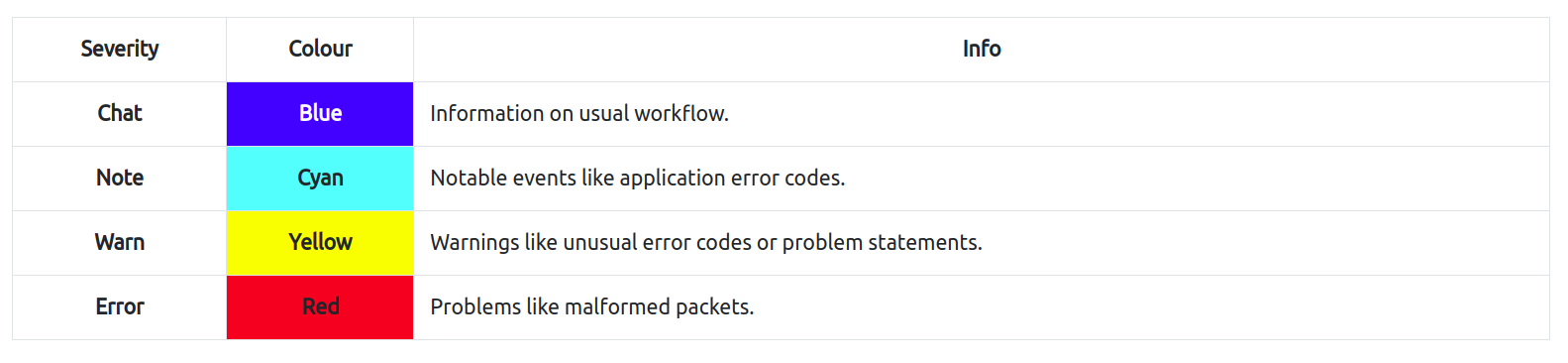
Colouring Packets
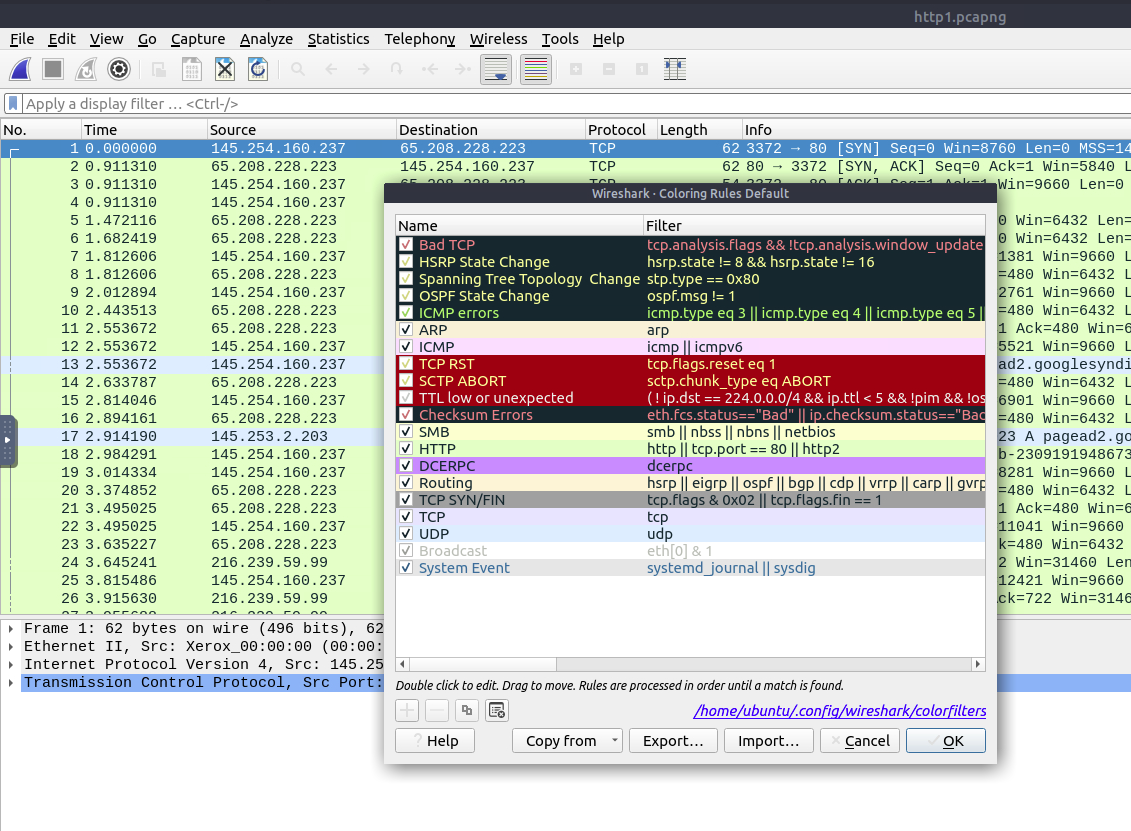
Wireshark colours packets in order of different conditions and the protocol to spot anomalies and protocols in captures quickly.
Packet Dissection
Packet dissection is also known as protocol dissection, which investigates packet details by decoding available protocols and fields.
Packet Details
You can click on a packet in the packet list pane to open its details (double-click will open details in a new window). Packets consist of 5 to 7 layers based on the OSI model.
- The Frame (Layer 1): This will show you what frame/packet you are looking at and details specific to the Physical layer of the OSI model.
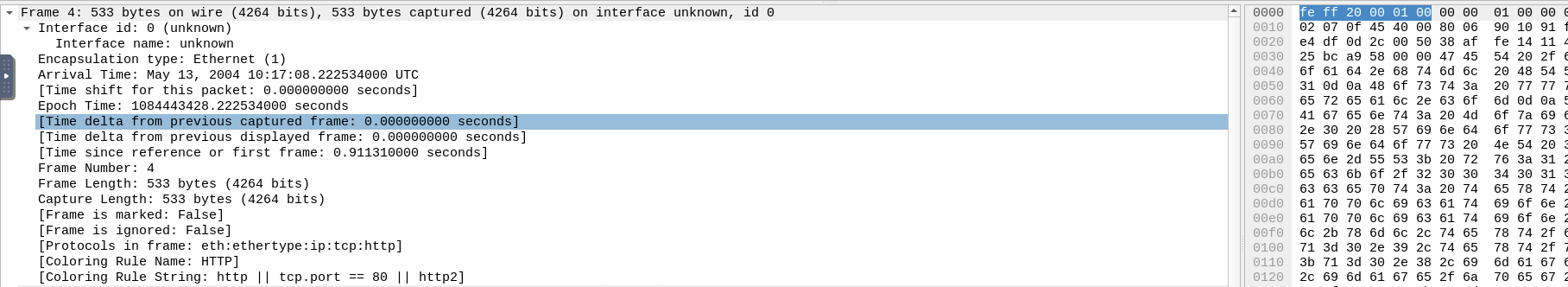
- Source [MAC] (Layer 2): This will show you the source and destination MAC Addresses; from the Data Link layer of the OSI model.
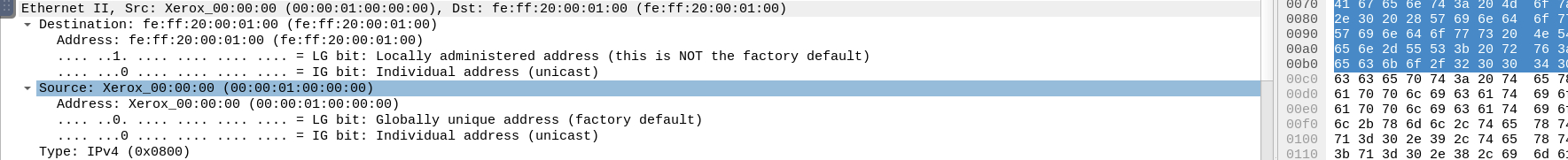
- Source [IP] (Layer 3): This will show you the source and destination IPv4 Addresses; from the Network layer of the OSI model.
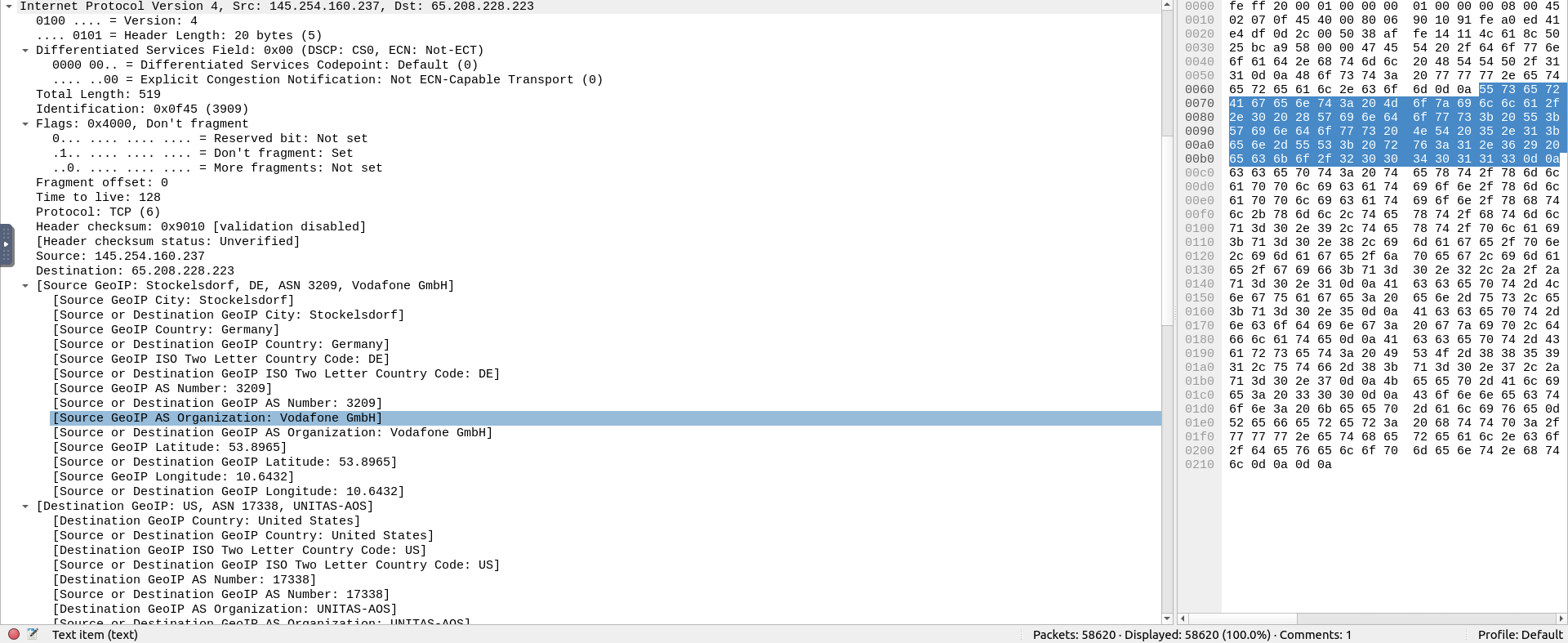
- Protocol (Layer 4): This will show you details of the protocol used (UDP/TCP) and source and destination ports; from the Transport layer of the OSI model.
- Protocol Errors: This continuation of the 4th layer shows specific segments from TCP that needed to be reassembled.
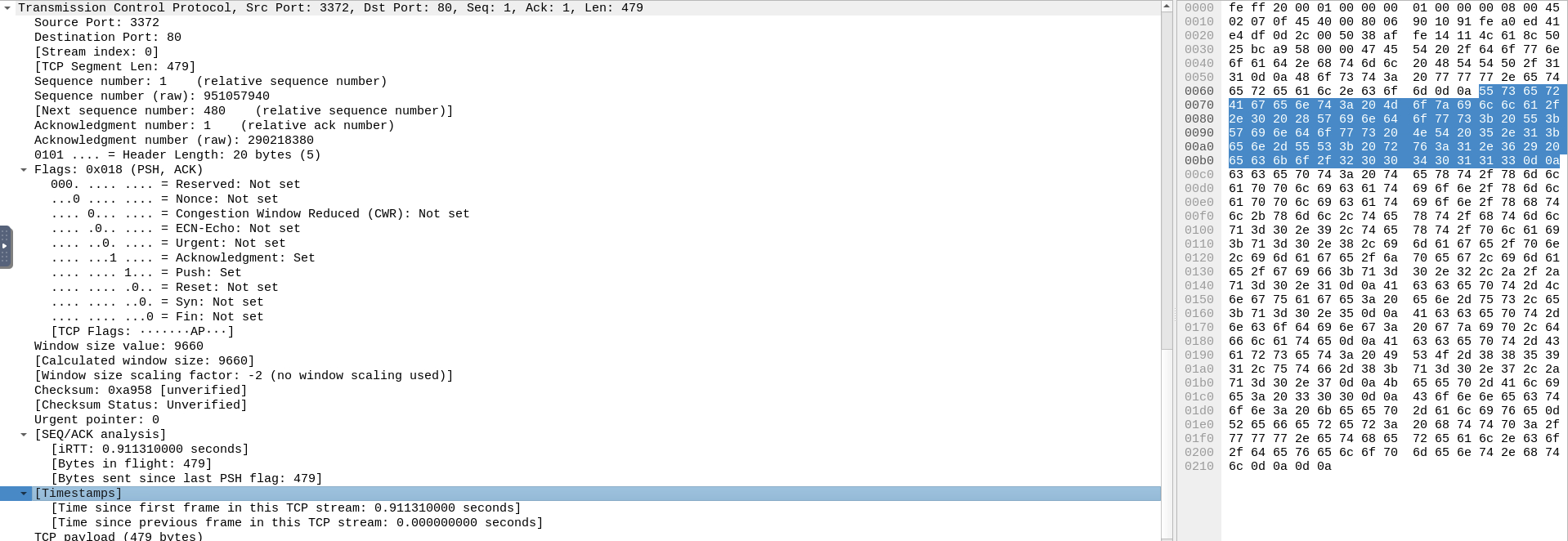
- Protocol Errors: This continuation of the 4th layer shows specific segments from TCP that needed to be reassembled.
- Application Protocol (Layer 5): This will show details specific to the protocol used, such as HTTP, FTP, and SMB. From the Application layer of the OSI model.
- Application Data: This extension of the 5th layer can show the application-specific data.
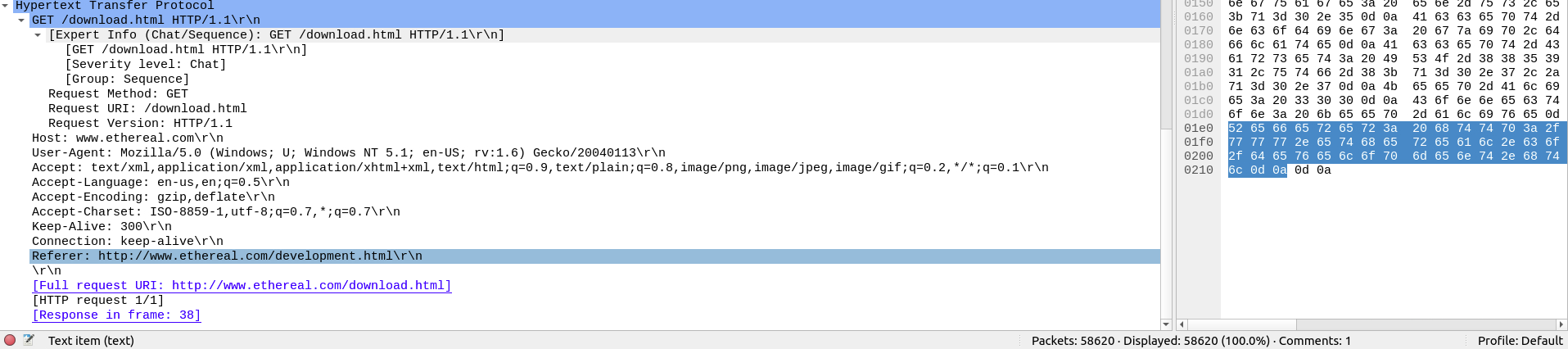
- Application Data: This extension of the 5th layer can show the application-specific data.
Packet Numbers
Wireshark calculates the number of investigated packets and assigns a unique number for each packet.
Finding them using Go to packet option under Go menu.
Mark Packets
You can find/point to a specific packet for further investigation by marking it. It helps pointing to an event of interest or export particular packets from the capture.
The “Edit” or the “right-click” menu can be used to mark/unmark packets.
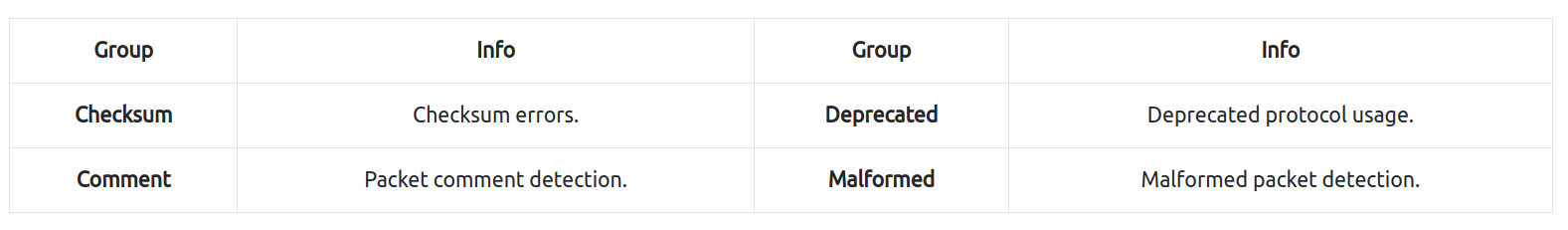
Expert Information
Wireshark can also detects specific states of protocols to help analysts easily spot possible anomalies and problems.
"lower left bottom section" in the status bar or "Analyse --> Expert Information" menu to view all available information entries